

I am against conscripts.
We must always be highly critical of those with power, money, and influence; especially governments and politicians (and the oligarchs that control/sway them).
I have known about those videos being posted on twitter.
I shared some of them last year, it is great that people are escaping the echo cambers we created for ourselves!
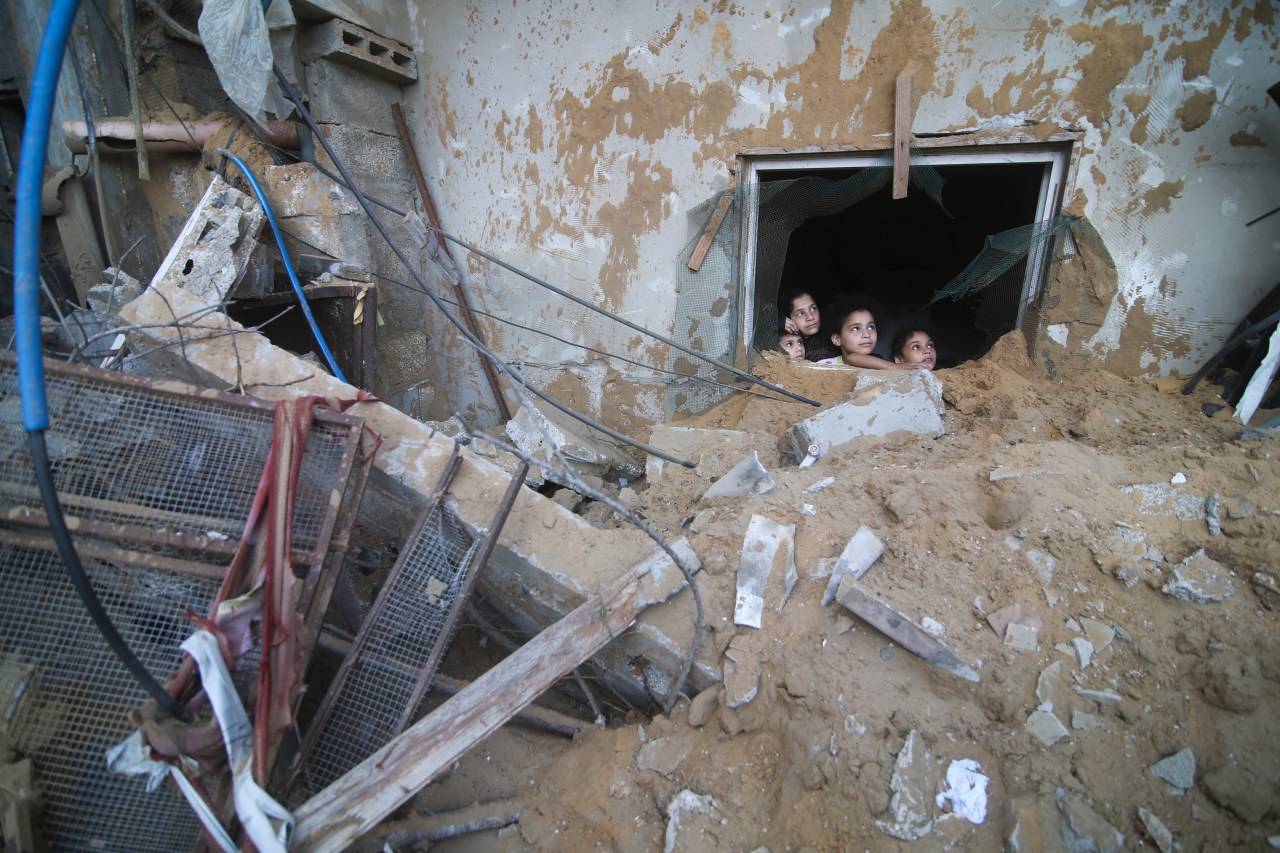
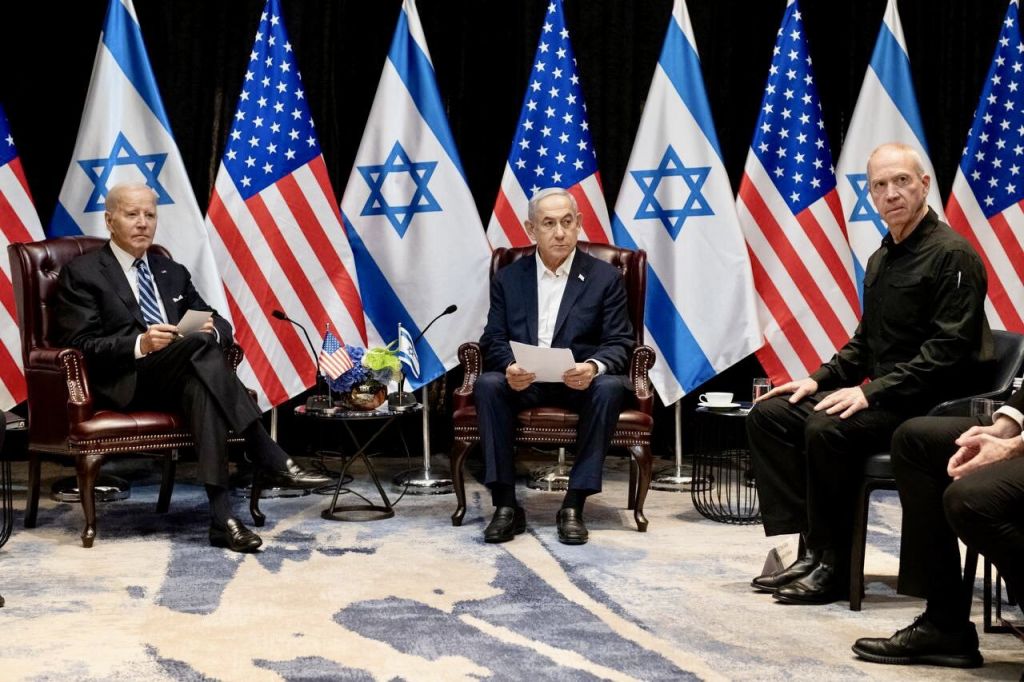
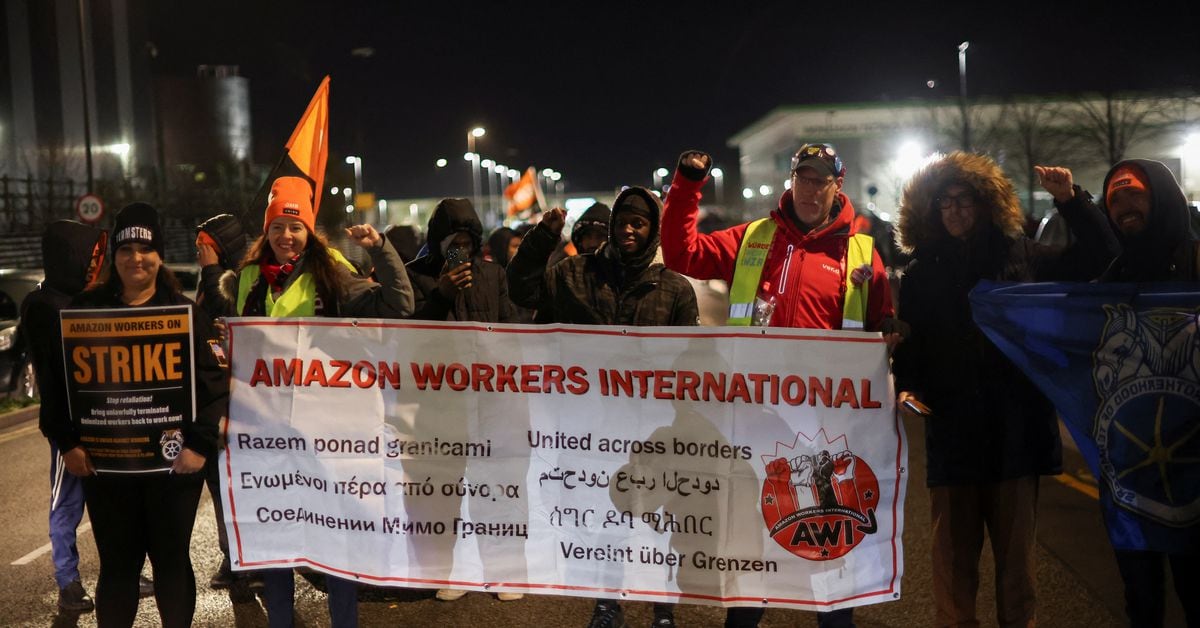
























By forcing your citizens to die for profit?
These endless wars will continue, since money has to be made, and corporations and oligarchs have a lot of sway when it comes to foreign policy.
The next war my country’s oligarchs and corporations are pushing for is with Iran and China; the duopoly is owned and funded by these corporations and oligarchs.