cross-posted from: https://lemmy.world/post/15565311
It was a long running project, but I finally did it. I built what I’m calling a smart mailbox that communicates locally with Home Assistant via ESPHome.
Parts:
- Pine plank roughly the width of my mailbox
- Treated pine plank for mounting
- Thin sheet of perspex or similar transparent plastic
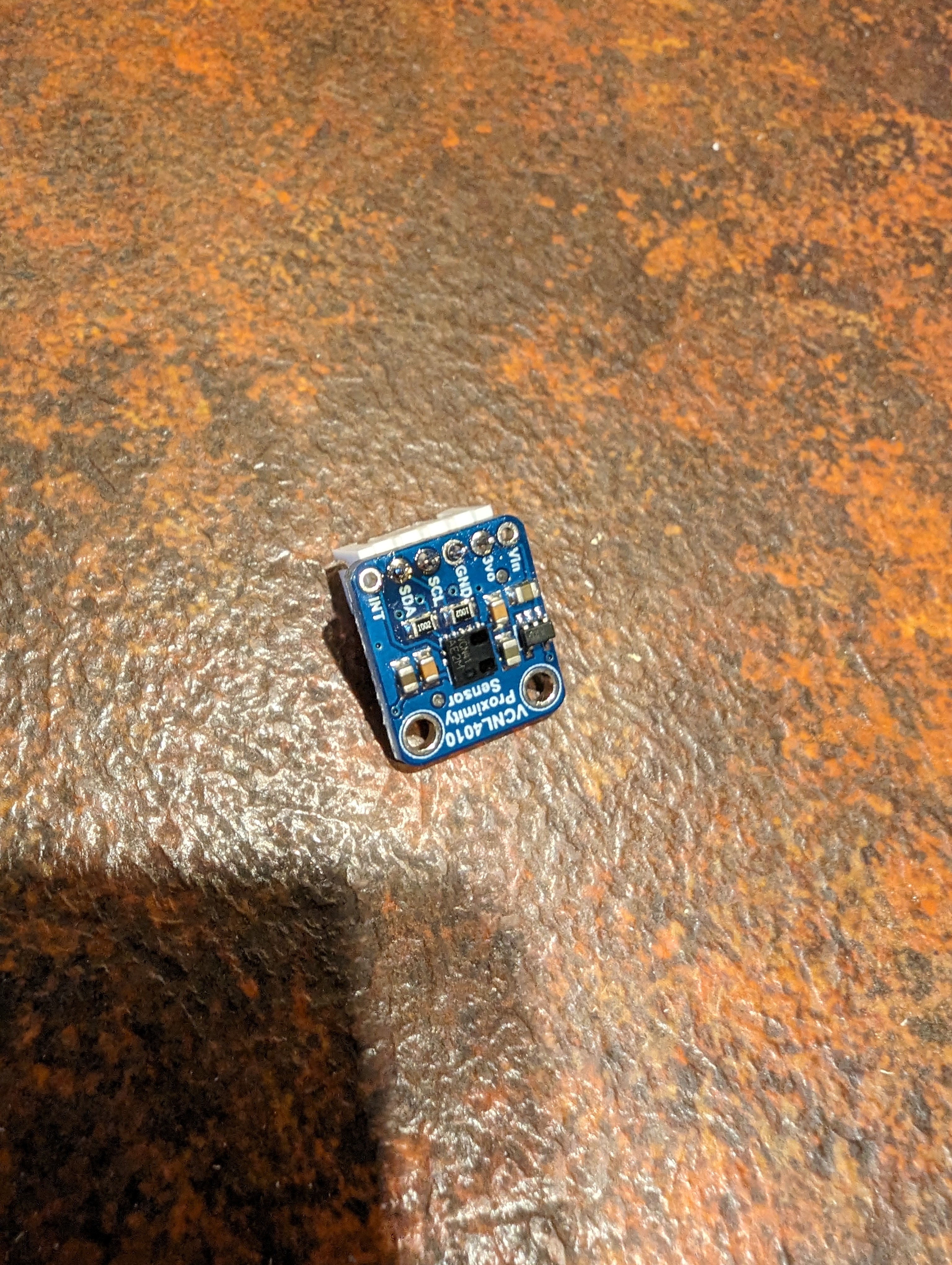
- 2x VCNL4010 proximity sensor
- ESP32 dev board with antenna
- Bigger antenna
- Prototype board
- 2.54mm pitch JST connectors
- 2.54mm pitch pin header sockets
- 18650 battery
- 18650 Type-C charging module
- Battery holder
- 2x 5V 1.5W solar panels
- MCP1700-3302E LDO regulator
- 100uF electrolytic capacitor
- 100nF ceramic capacitor
- Resistors… I think I ended up using a 1 MOhm and a 330 kOhm
- Weatherproof junction box
- Nylon screw spacers
- Cable glands
- 12mm waterproof button
- Various cables and wires
- Paint and polyurethane spray to weatherproof the wood
Tools:
- Soldering iron
- Router for cutting grooves in wood
- Drill and hole saw bits
- Various files and sandpaper
For a start, I followed this guide to get me started on the power delivery portion, but I ended up using much higher valued resistors since I found that I was losing more battery charge through the voltage divider than I was from the ESP32 or proximity sensors.
Once I’d tested the concept with the parts just laying in a jumble on the table, it was time to get to work.
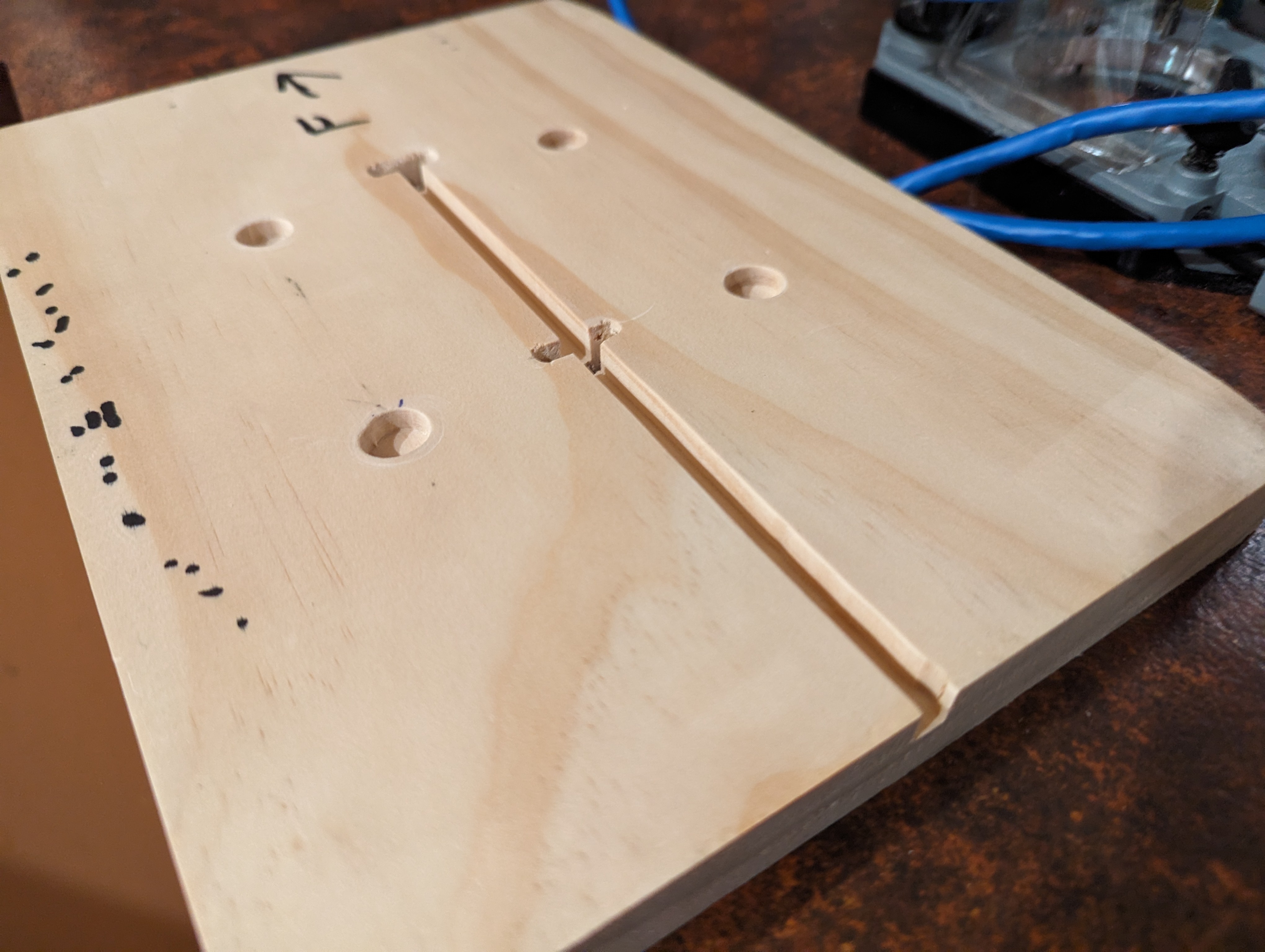
I started by cutting a plank of pine to fit my mailbox, chamfering the ends to make space for the metal joins. I routed out some spaces for the tops of the bolts that hold the mailbox down.
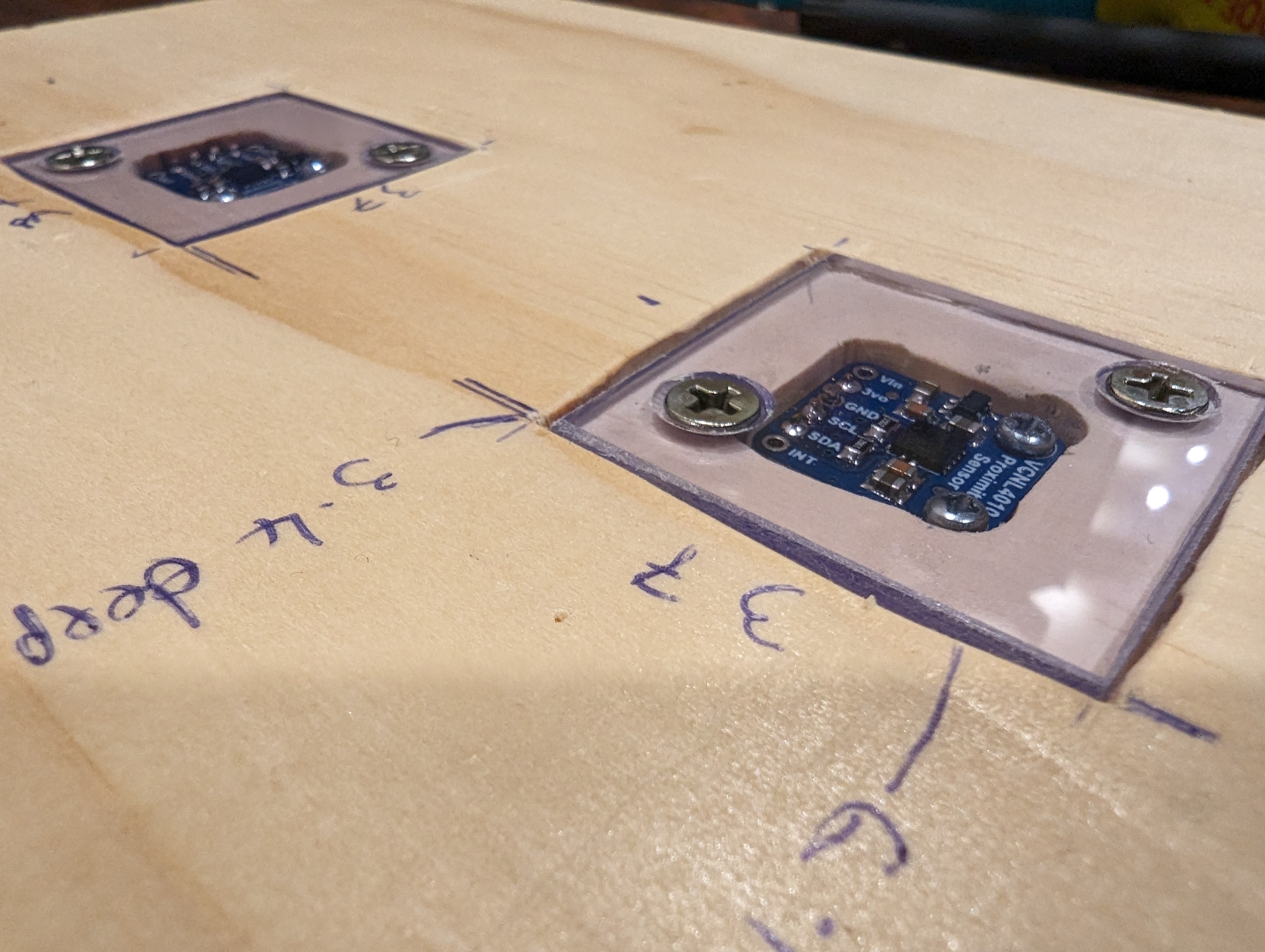
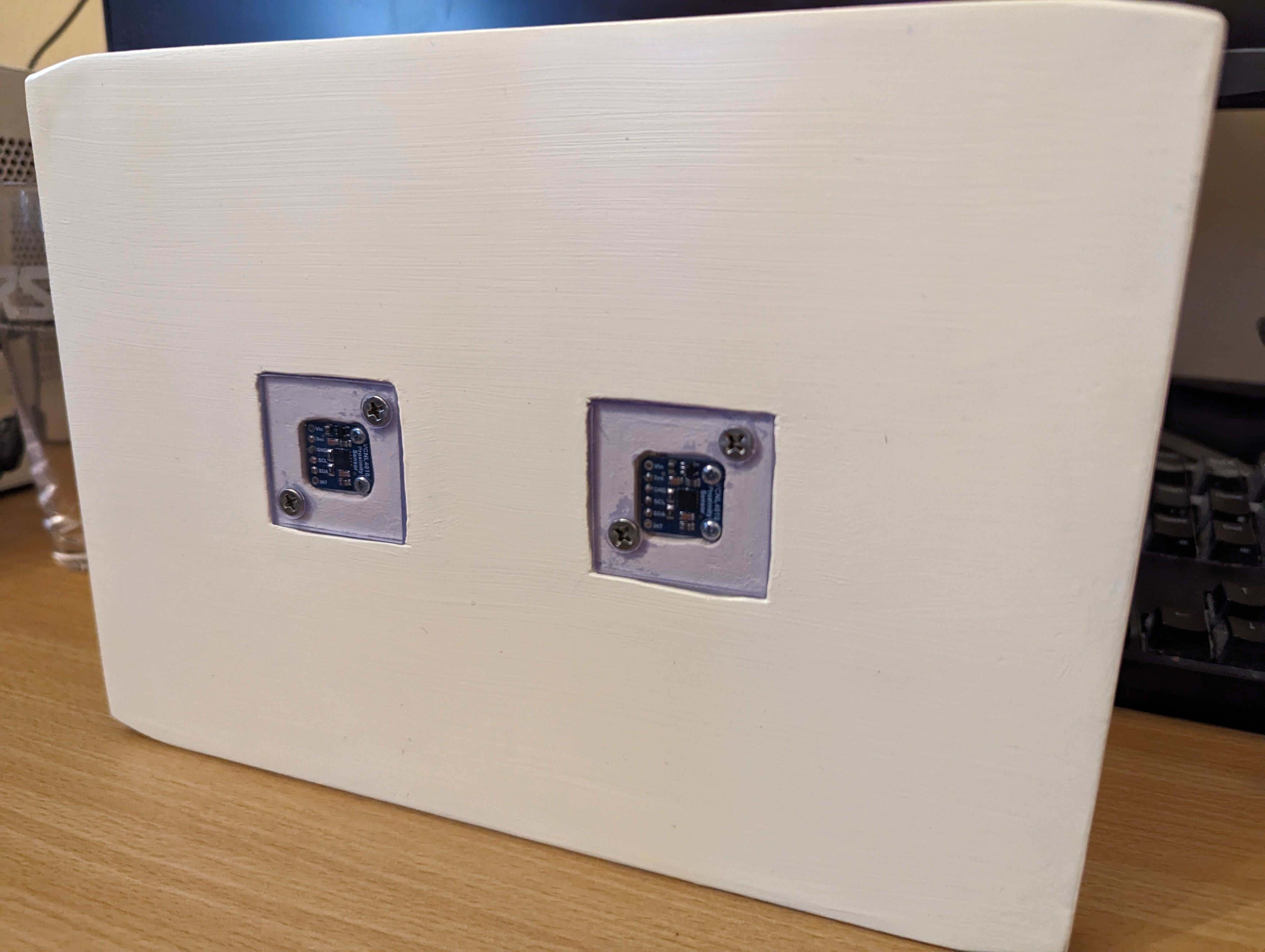
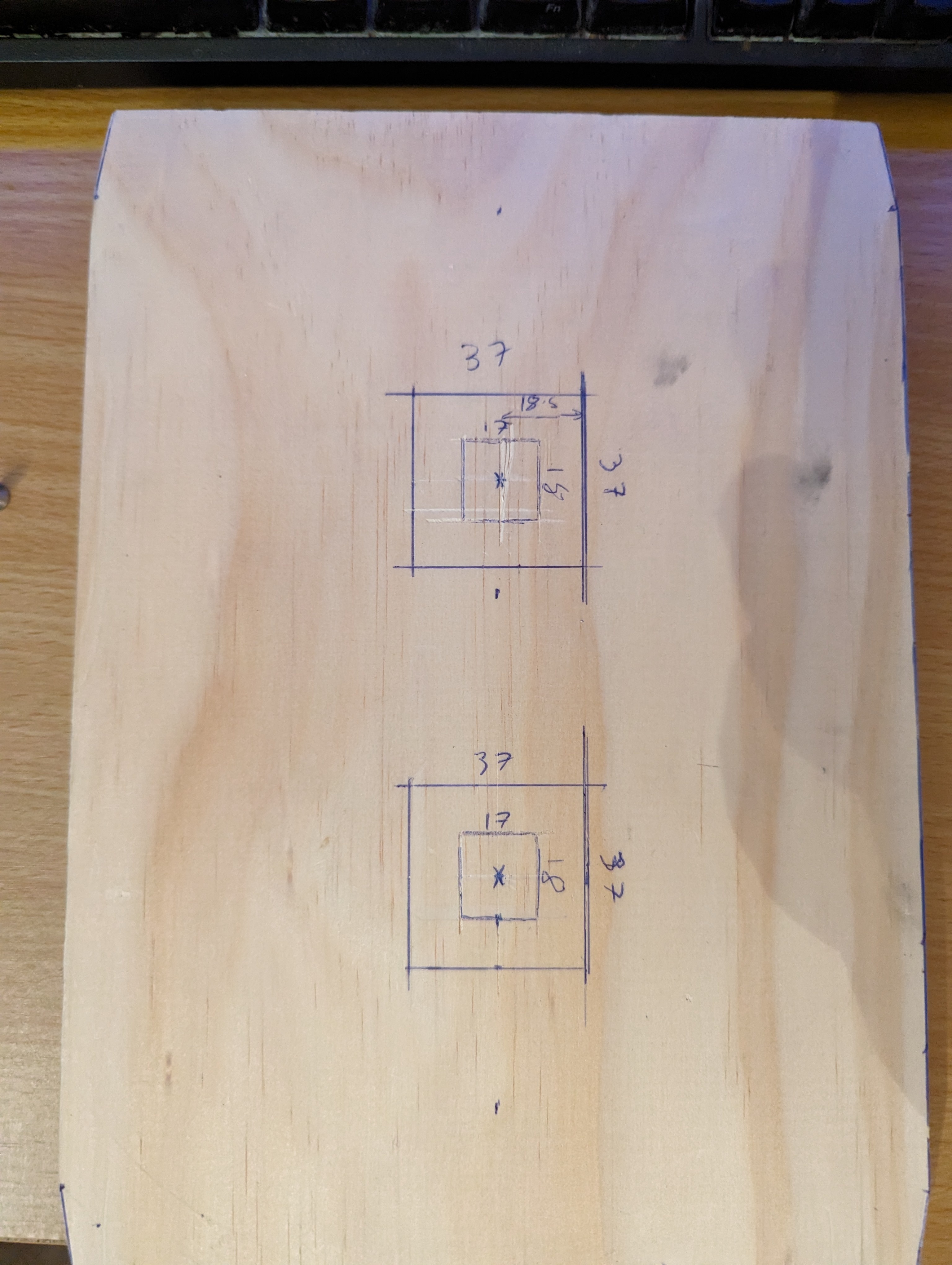
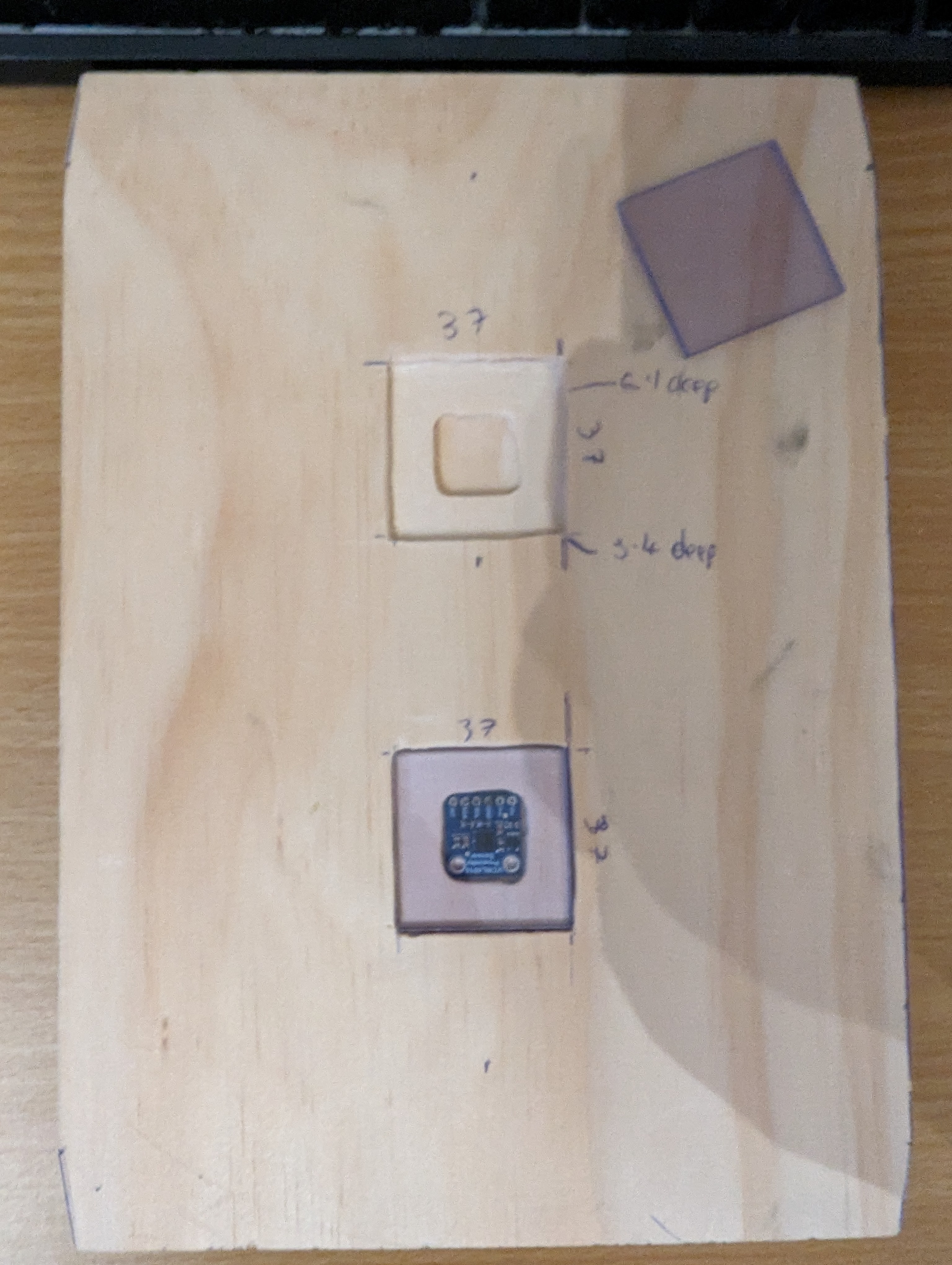
Measured out where the sensors should go, along with a surrounding space to screw down some little perspex windows to cover them. The idea I wanted was for the mail to be able to slide over the sensors without getting caught on them, as well as to protect them from dust.
Routed out the dents and cleaned them up with a chisel and sandpaper. Cut the perspex to shape for a test fit.
On the other side, I routed out a notch for the cable to access the sensors.
I had originally planned to just solder wires into the sensors, but then I realised JST connectors would fit perfectly into the sensors. This meant I had to widen the holes somewhat, which I did with a small chisel and file.
I got a bit lazy with making screw holes to hold down the perspex, so they’re not in as neat a place as I’d like. If I did this again I’d measure properly for their placement. Still, with countersinking they hold down the perspex well and nothing sticks up for mail to get caught on.
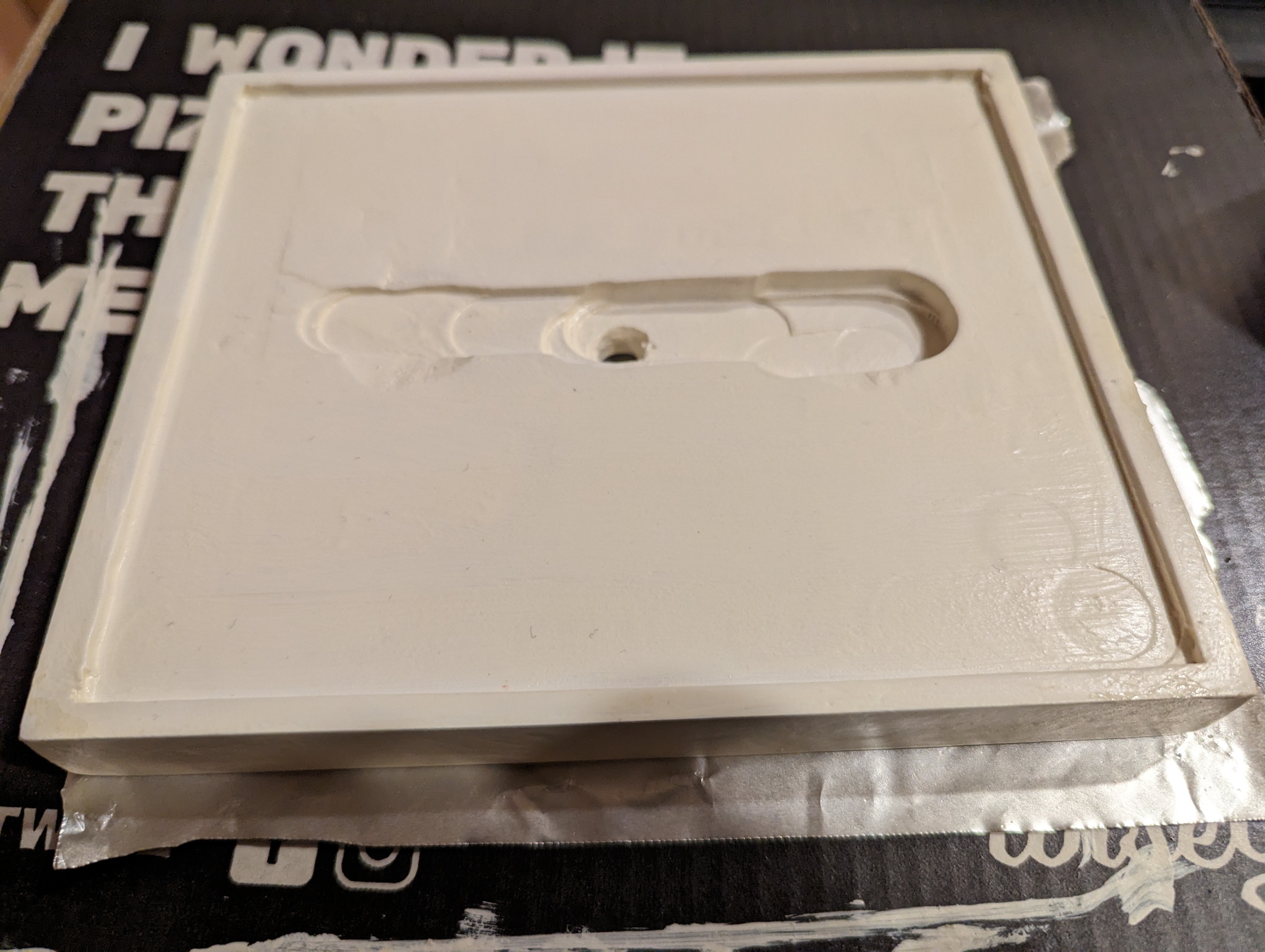
I also got started on making a housing for the solar panels. I used the router to carve out a 1-2mm area for them to sit in, and a much deeper ditch linking the two terminals, which you’ll see in a later picture. For now, here’s how they look sitting in it.
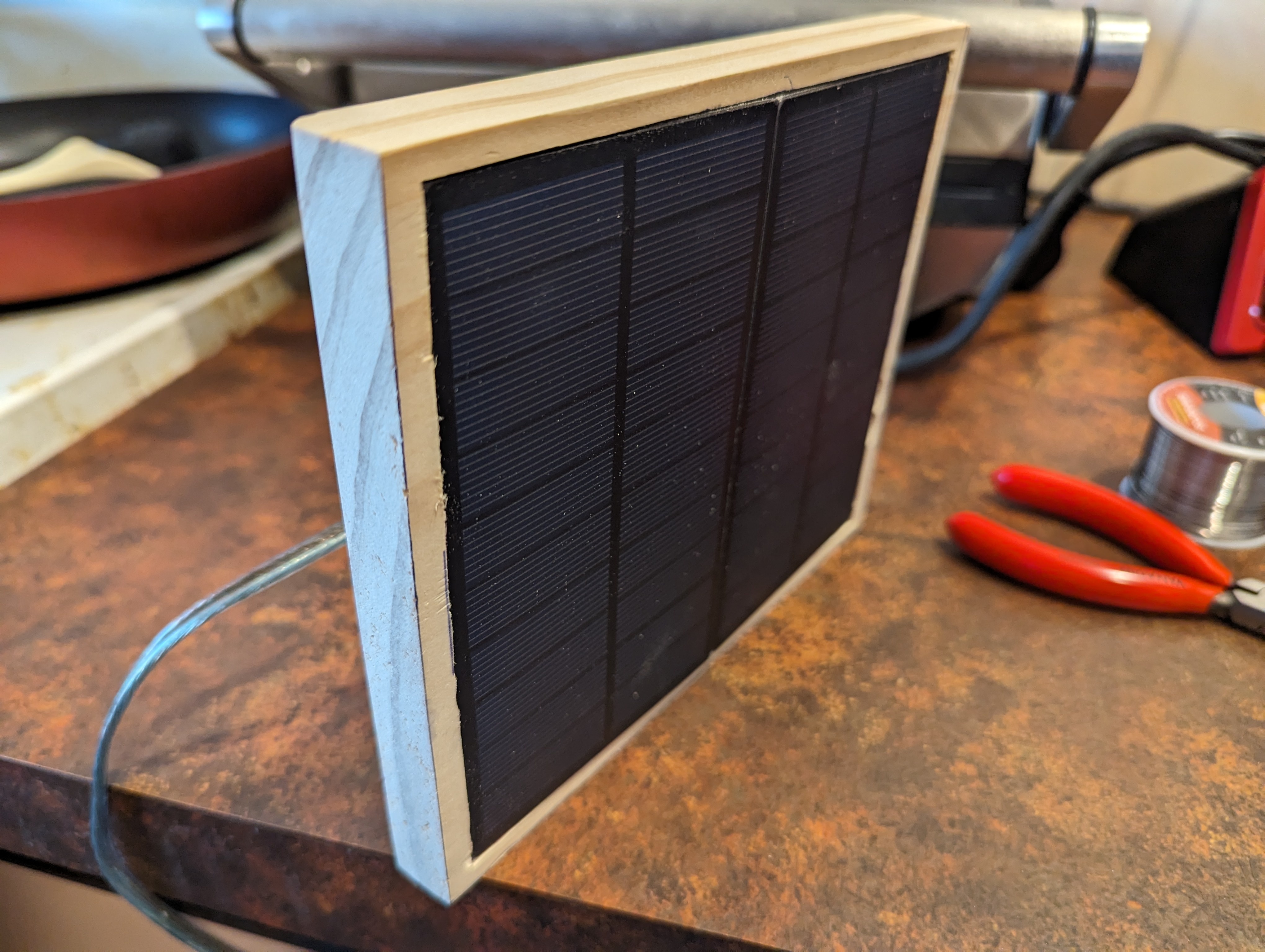

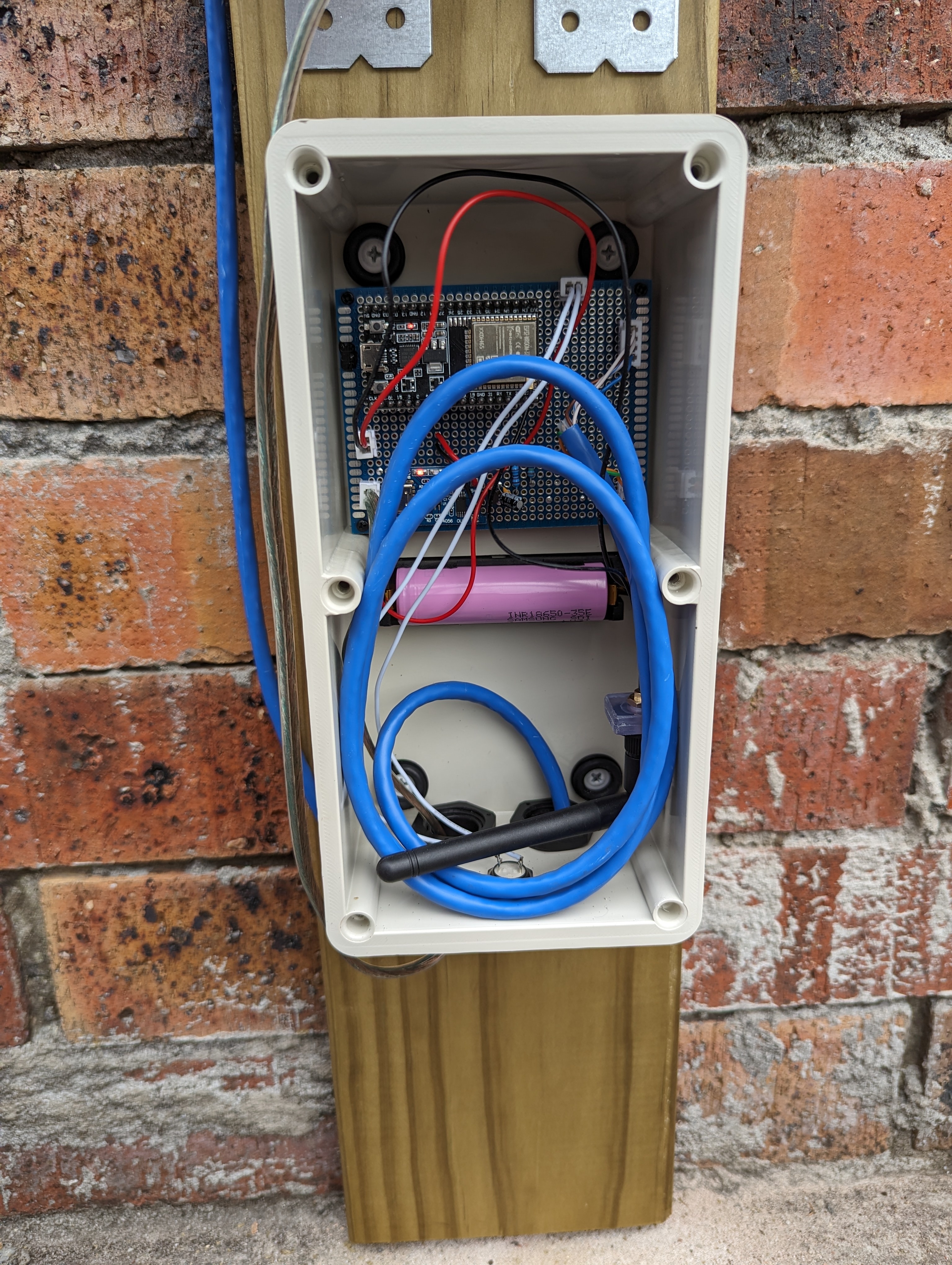
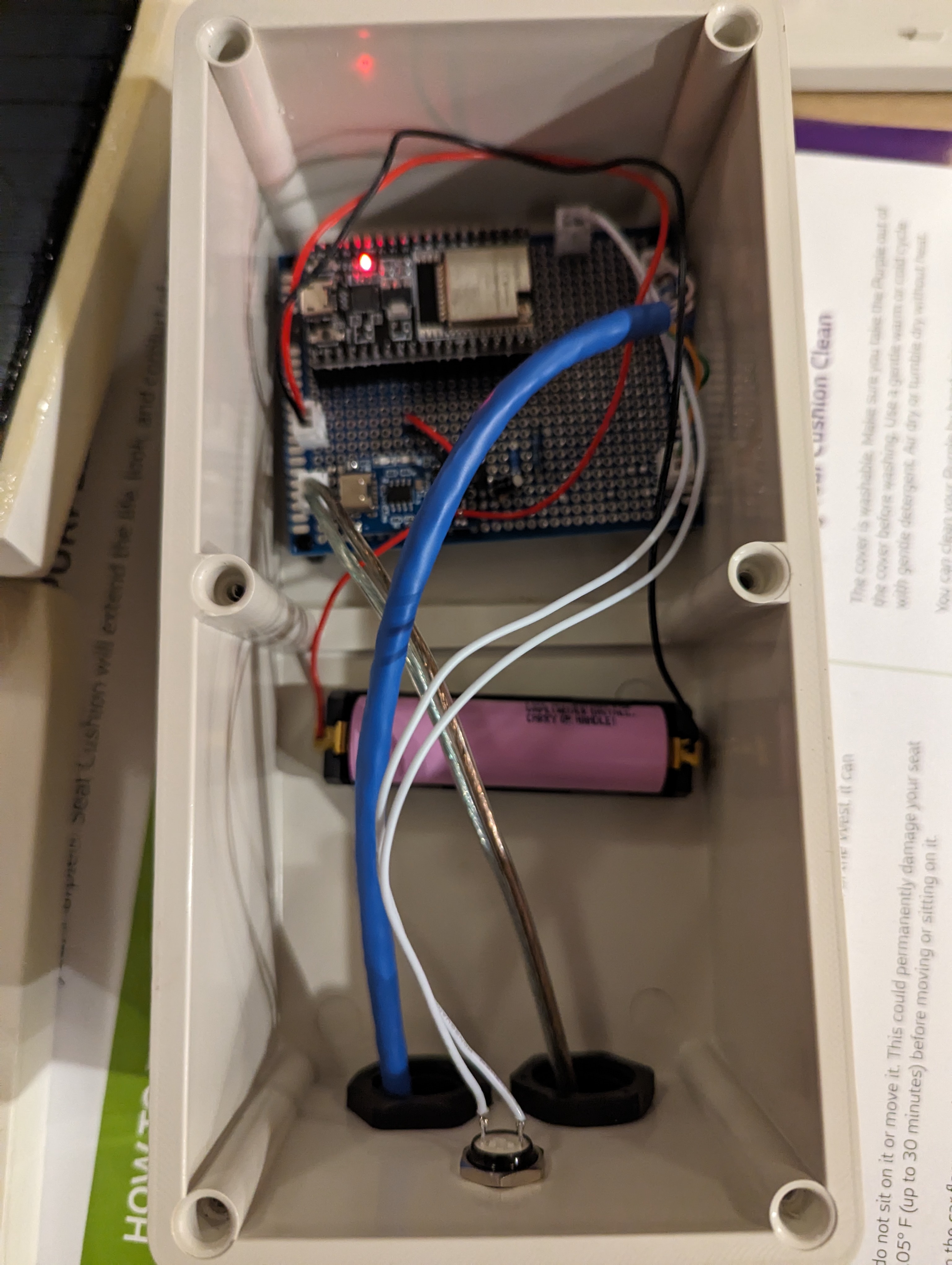
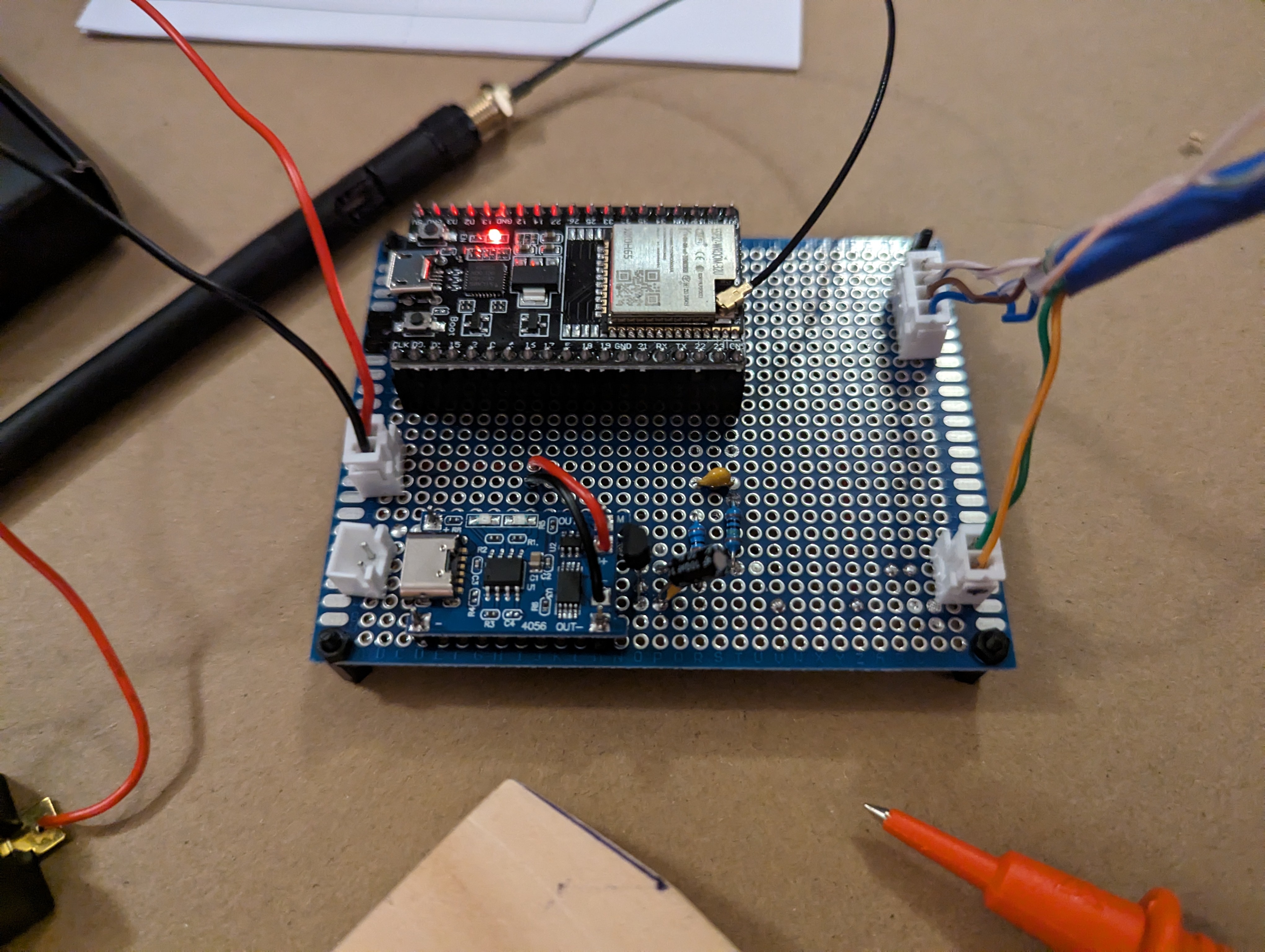
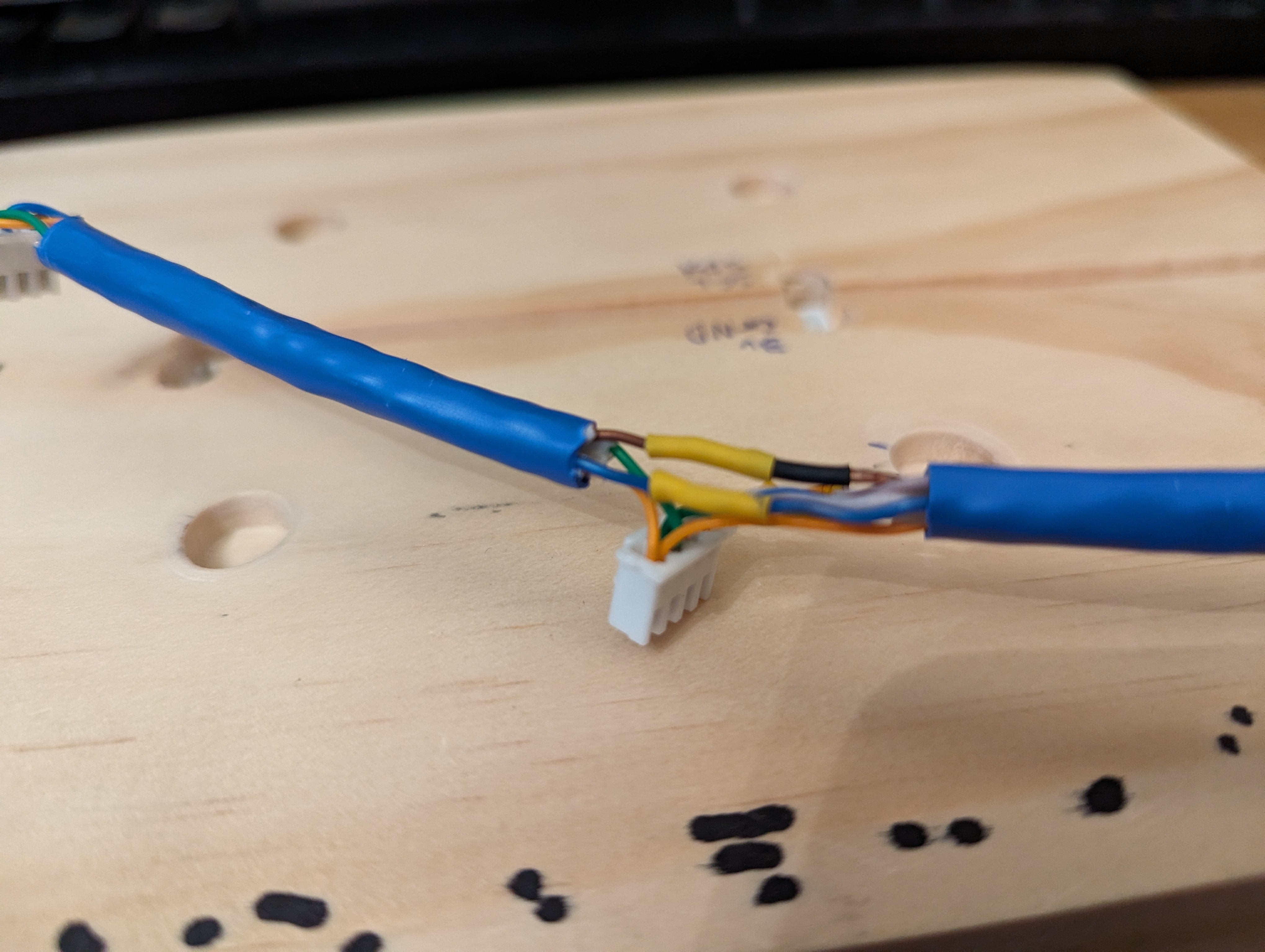
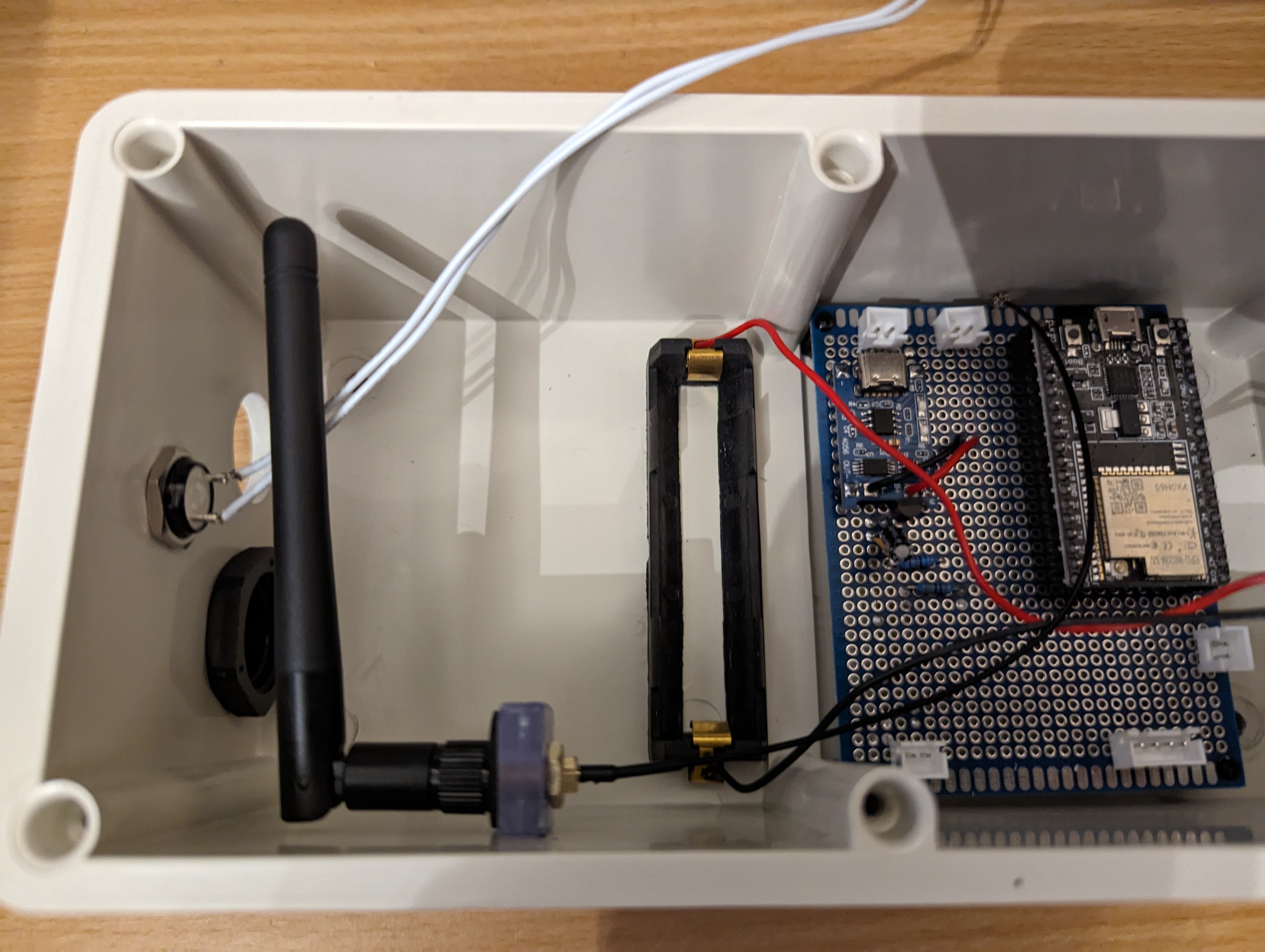
Wiring up the prototype board was next. Again, see the article I linked above for how this works. I used pin headers to allow the ESP32 dev board to be slotted in and out, just in case I ever needed to take it out for replacement or reprogramming. Also the JSTs on the prototype board are for connecting the battery (top left), connecting the solar panels (bottom left), providing power to the sensors (bottom right) and clock and data lines for the sensors (top right). Since the sensors are both using the same I2C bus address and cannot be configured otherwise, I had to run two clock and data lines, but if I’d found sensors that could have different addresses I could have just used one of each. I didn’t take a photo of the board at this stage, but I later added another header to connect a button to reset the ESP32 from the outside.
I also made the data and power cable for the sensor board.
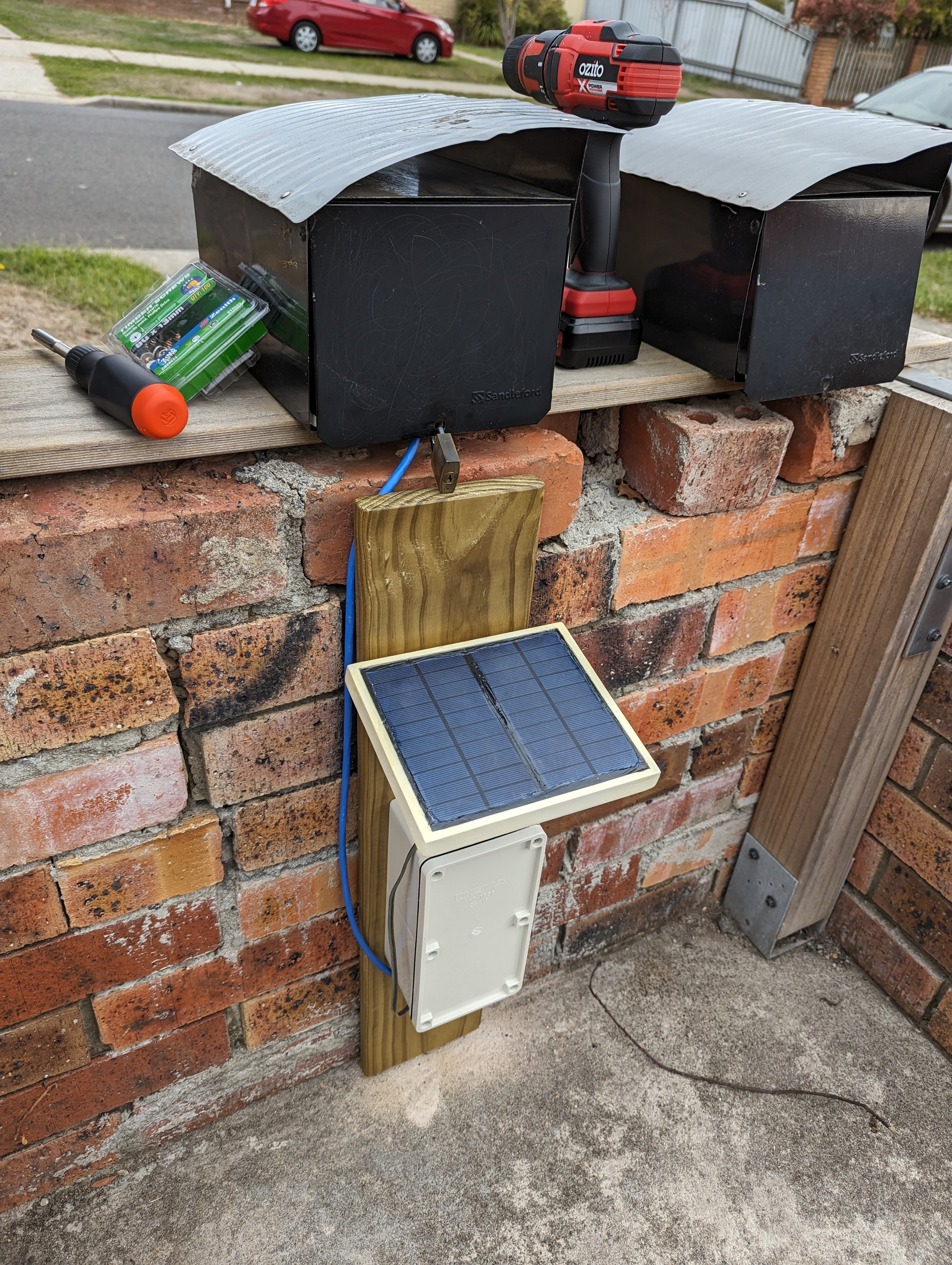
The solar panel housing and ‘sensor plate’ were both painted and treated with polyurethane spray to protect them from rain and humidity.

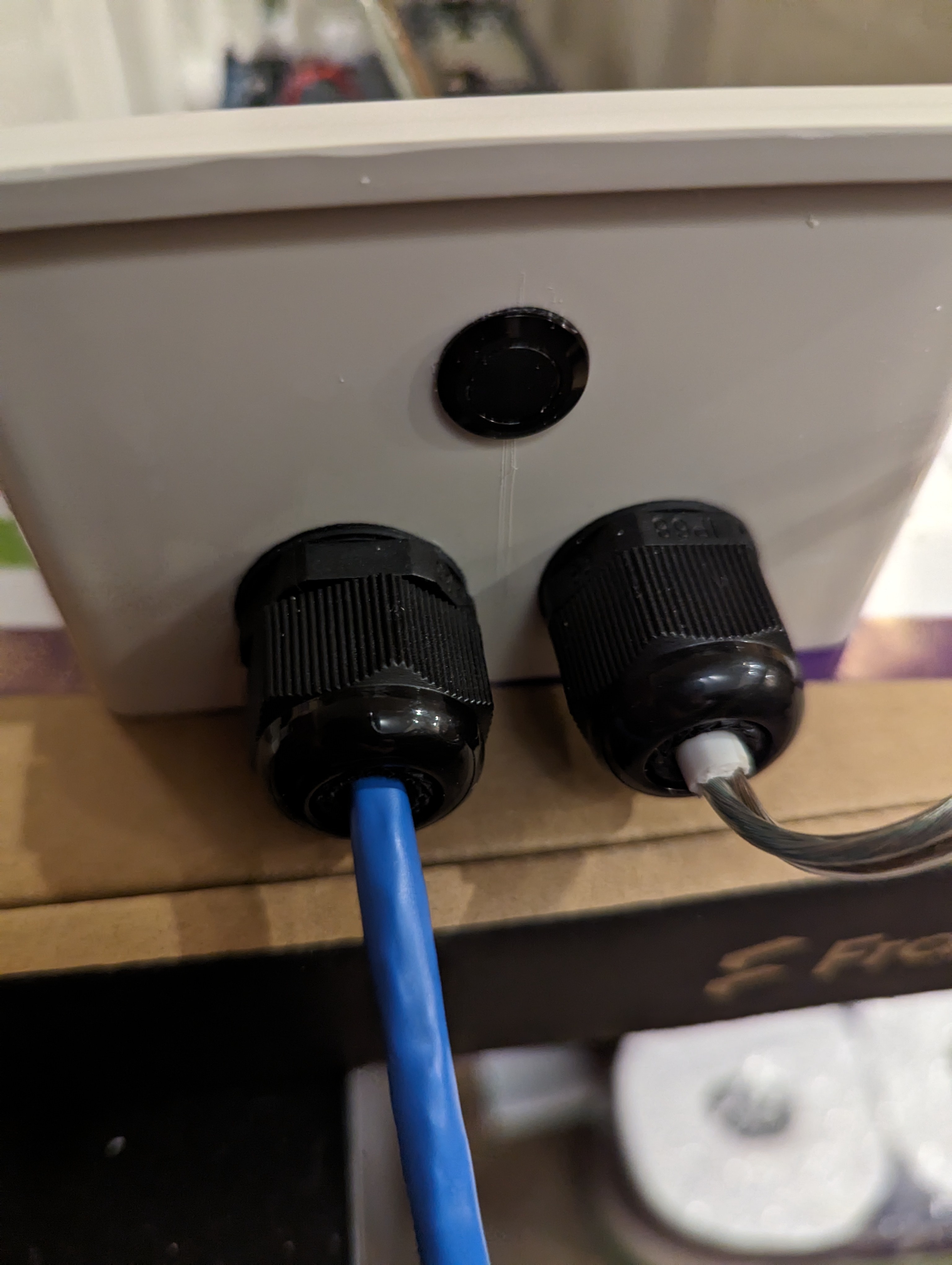
I drilled holes in the weatherproof box to fix the cable glands and the weatherproof button. In the case of the solar panel wire, I had opted to buy speaker wire since I figured it would be easier to run in the channel between the two solar panels, being flat. But that also made it not really fit the cable glands that great. I ended up stripping some of the outer sheath off some 2 wire power cable I had, and wrapping that around the part of the speaker wire that gets clamped in the glands, just to make a reasonable seal. These all were on the side I decided I would mount at the bottom, so water wouldn’t be able to easily fall into the box.
Final test fit. I later used epoxy glue to glue down the nylon headers and the battery holder inside the box.
The mailbox itself also needed a hole in the bottom for the sensor cable to come out. After drilling a hole and filing it into a square shape, I cut some rubber grommet strip to size and fitted it around the hole, with some marine silicone adhesive to protect the sharp metal edges from water and to hold the grommet strip in place.
I’d drilled some holes in the brick wall my mailbox sits upon for masonry anchors, and this piece of treated pine got the last of my polyurethane spray, just in case.
Using a two pieces of the leftover perspex glued together, I made an internal mount for the antenna, figuring it would be best to not have the thing either floating around freely inside the box or sticking out the side where people could potentially break it off.

Finally, after weeks of off and on work, it was ready to install.
The ESPHome coding used my VCNL4010 component, and if anyone is interested I can share it but it’s kinda a large file.













Yes exactly, when looking for it I find only Arduino kits. Some time ago I got interested in pine64, was reading a while and bought a soc board plus some stuff around it (like a touch screen and emmc storage). Turned out that particular board didn’t come with the display output and to install a system on emmc you need an UART Adapter, so I ended up buying more stuff, which I was missing. Don’t want to do the same again ^^
With esp32 I have the problem that there are so many different and I don’t see how they differ (except the price)
Okay so that is an issue with the ESP32, sure. There are a lot of variants.
So from what I can tell, the ESP32 is the SoC chip and what you usually get is a dev board which has that plus a bunch of power regulation bits, a USB connector and UART so you can easily program it, etc. That part varies mostly by pinout. I.e. Same features, different pin location.
There are also variants of the chip, but those are usually more costly and will be named things like ESP32-S2.
Every one I’ve seen can run off 5v or 3.3v and uses the latter for logic, so if you got yourself an arduino kit and then just bought an ESP32 dev board it would almost certainly work with whatever is in the kit. Both are microcontrollers, not microprocessors, so they tend not to have OSes or screens.
Thank you, that helps a lot. This kind of hardware introduction is missing on esphome.io :)
No problem. The one I used is an ESP32 DevKitC, and you can find info about it on Espressif’s site, or just google the pinout diagram. For basic tasks it should be all you need since it has lots of binary pins, two ADC channels, two DAC channels, realtime clock, special pins for waking it from deep sleep, two I2C, etc. Though if you want to do video input you probably want something else, I’m learning.
Anyway, if you can spare the money to get one just to toy with I’d definitely recommend it.